Claris is ushering in a new era of FileMaker by integrating advanced AI capabilities, making intelligent, custom app development more accessible than ever. With powerful models like OpenAI’s GPT-5 and GPT-5 Mini now available directly in FileMaker, AI is quickly becoming central to how teams build and work. At DB Services, we've been putting these innovations into practice, primarily through AI-powered chatbots that interact with FileMaker data to streamline tasks, reduce errors, and deliver instant insights across customer service, accounting, operations, and technical support. In this article, we’ll dive into how these chatbots enable human-like, conversational access to your data, and walk you step-by-step through how the full FileMaker + AI setup works.

The Vision: Human-Like Support Powered by FileMaker
Imagine you're a customer support representative who needs to access a client's order history. Instead of digging through menus and portals, you could ask the system:
"What was the last item John Smith ordered?"
Perhaps you're in accounting, reviewing discrepancies at the end of the month. Rather than cross-referencing totals manually, you can ask:
"Show me invoices with mismatched line item totals over the last 30 days."
Or maybe you're on the phone with a client and want to recommend they try a product related to their previous orders. Instead of reviewing their sales history in detail live on the phone, you could ask:
"What should I recommend to Jane Doe that she has never tried?"
In each of these scenarios, AI doesn't just save time—it empowers users by giving them immediate access to the answers they need. When appropriately integrated, AI becomes a conversational interface to your database, unlocking new efficiencies across departments.
How It Works: Integrating AI into FileMaker
Getting started with FileMaker + AI is easier than you might think. Claris has introduced many new functions and script steps; however, this example file here primarily uses steps that will be familiar to anyone who has worked with APIs. Check out our article on Insert from URL using cURL to break down how to use this feature.
The agentic AI behavior comes from the data structure and scripting organization. Here's how the setup works in broad strokes:
Step 1: Get Your API Key
First, you'll need a paid OpenAI API key. This example utilises Model 4.0, which delivers high-quality, conversational responses and performs effectively with structured data queries.
Step 2: Configure Your AI Account
FileMaker includes a built-in script step: Configure AI Account
Here's how we use it:
Account Name: "default"
Model Provider: OpenAI
API Key: Your personal or organizational key
Once configured, you're ready to create your first agent.
What is an Agent?
In an AI context, an agent is a chatbot persona with access to a defined set of tools and instructions. Each agent is instructed to fulfill specific tasks and can only interact with the tools you assign.
Agents can be tailored to different job functions or permission levels. For example:
A customer support agent can pull order information, open support tickets, and send emails.
A warehouse agent might only have access to shipping and inventory tools.
An accounting agent could interact with financial summaries and invoice data.
By limiting what each agent can access, you enhance both security and ease of use.
What Are Tools?
For this purpose, tools are FileMaker scripts that your agents can use to accomplish specific tasks. We use scripts over custom functions because they enable agents to take actions with precision, such as targeted searches or updating records.
Each tool is defined by:
A script that performs the action
A description in plain language that describes what the tool does
Parameters that feed data into the script
Here are some example tools:
GetOrderInfo
Description: Given an order number, this tool returns relevant data about the order.GetCustomerInfo
Description: Given a customer name or contact name, this tool returns relevant data about a customer and associated order numbers.SendEmail
Description: Opens the user's email client with a pre-written email given the parameters.GetSupportTicketInfo
Description: Given a service ticket ID or contact name, this tool returns relevant data about a service ticket.
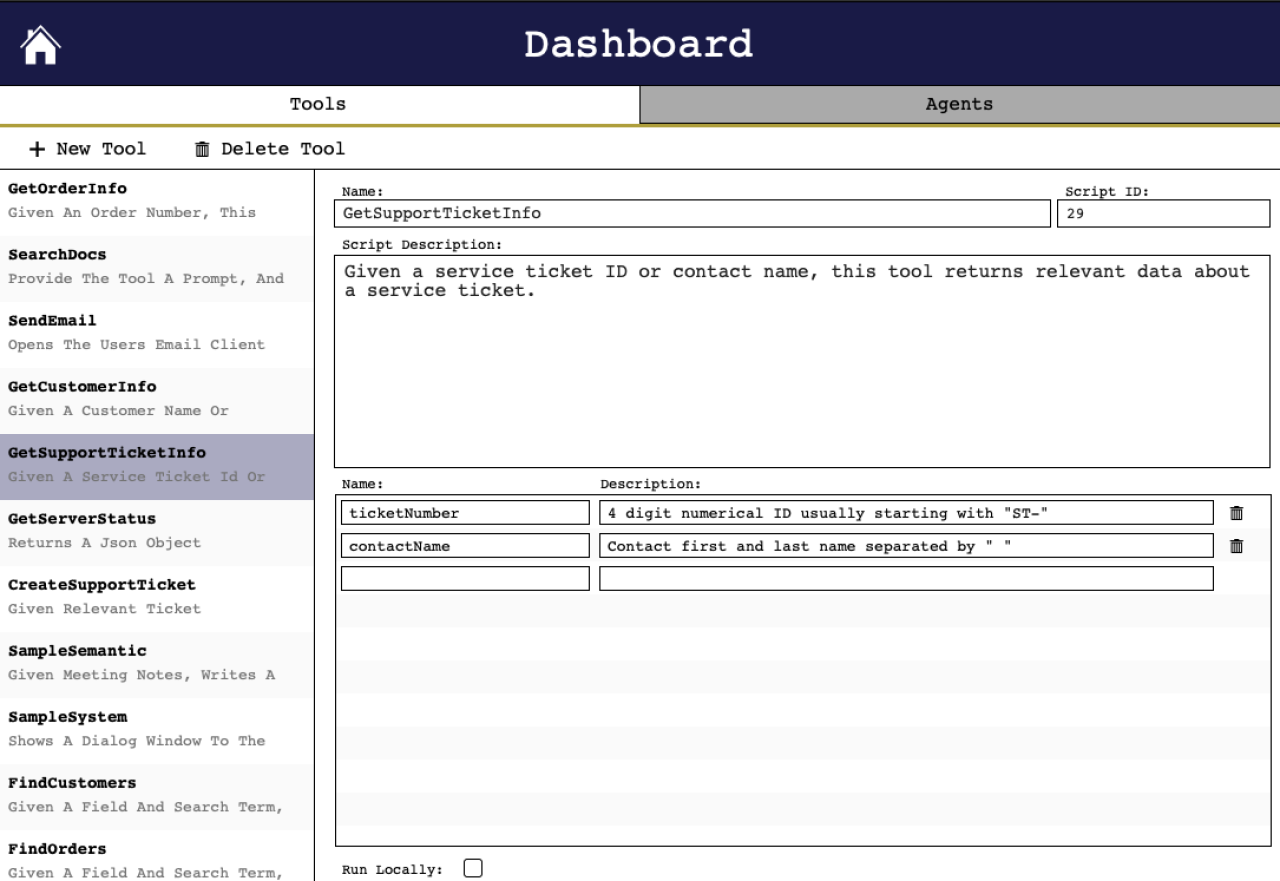
These tools act like extensions for the agent. You can create as many as you want and make them as complex or as simple as your workflows require.
Creating Custom Tool Scripts in FileMaker
To build your own tool, start by defining the parameters the AI needs to pass in. For example, a simple "Find Order by Field" script might use:
Field Name
Search Term
In the script, you can then:
Use
Set Field By Nameto target the specified fieldPerform a
Findon theOrderstableReturn the results to the AI agent
Because the AI can dynamically pass parameters, your tools become highly flexible. You can search by order number, customer name, status, or any other indexed field in your solution. And as your business logic grows more complex, so can your tools.
A few rules of thumb for creating tool scripts:
Make your scripts modular: they could be called from any context or any found set.
Test your scripts thoroughly. Check out our primer on testing your work to get started.
Handle errors effectively.
Return results in a consistent format.
Use JSON for script parameters and results.
Assigning Tools to Agents
Rather than have one all-powerful agent, create unique agents to perform specific functions. A simple tool like Search Orders may be used by many agents for various purposes, but a tool that sends emails or checks employee information may be limited to one or two agents.
Each agent requires clear instructions that define its job. These instructions, combined with the prompt from the user, will determine how the agent utilizes the available tools.
Consider a physical example: If one agent is tasked with building a house, and another agent is tasked with filling a jar, both agents might utilize a tool called "Select Nail." The agent's instructions will change how and when that tool is used.
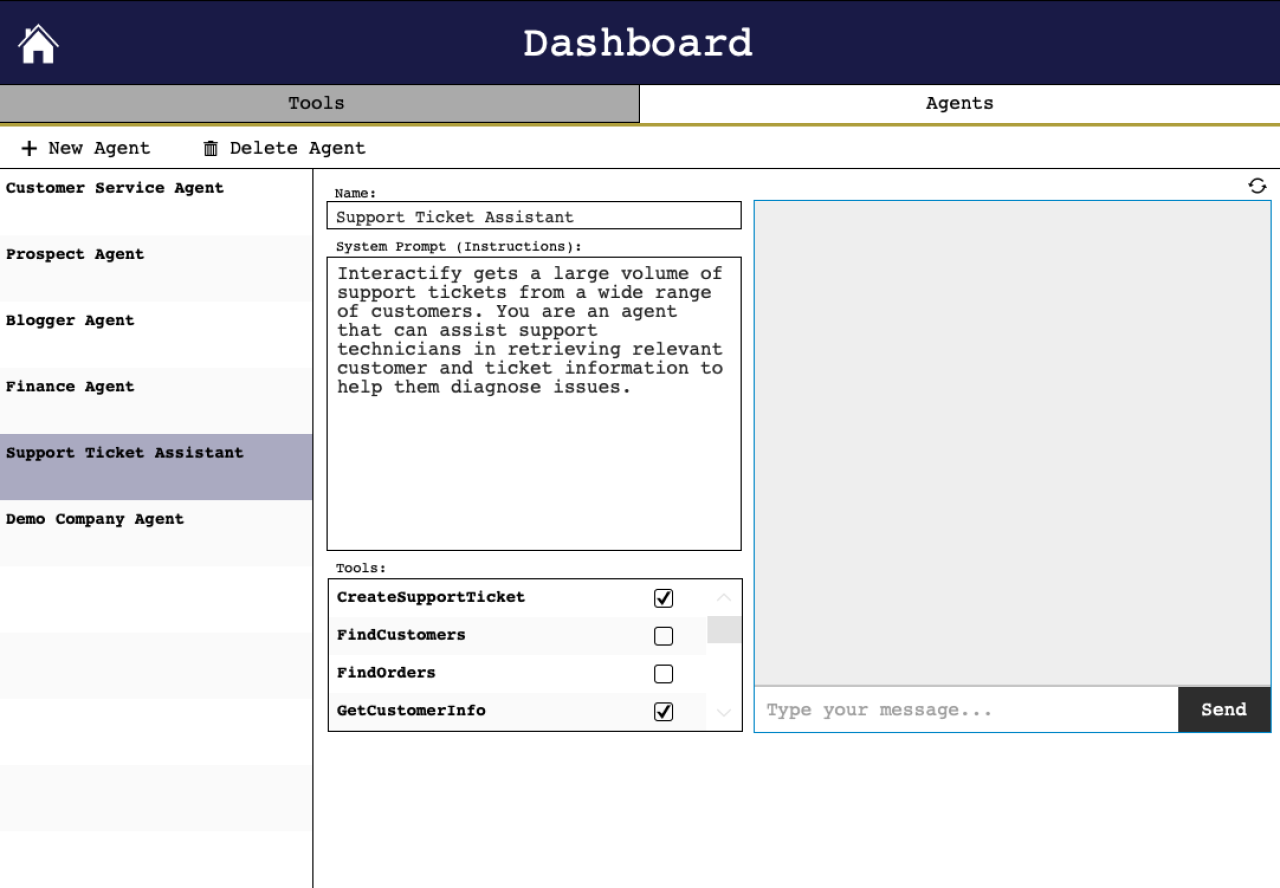
Here are some example instructions for agents:
"You are an agent who can assist support technicians in retrieving relevant customer and ticket information to help them diagnose issues."
"You are a blogger agent. Our marketing team frequently writes blog posts to promote new features as they launch. You are an agent that can support this process by gathering accurate product information and drafting marketing deliverables like emails, blog posts, etc., with the same voice as the company's other marketing materials on the website."
"You are a finance support agent. We've had an increasing number of data entry issues related to billing. This creates confusion, delays in reimbursement, and unnecessary escalations to Finance. We need an agent that can identify/diagnose these issues and allow the user to follow up with affected customers directly to make it right."
Numerous online resources are available to help you craft effective instructions and prompts for AI. The examples above should be considered starting points. For any real-world use case, you can expect to refine your instructions over a testing period to achieve better outcomes.
Generating a Response
Creating a final response to a user is an iterative process. In many cases, a single prompt may require multiple API calls to obtain a final answer. The initial call sends the user's query along with all of the available tools at the agent's disposal. The first response from the model is generally a request to call specific tools with specific parameters. From there, we run those tools and send the results back to the model, which will then either send a response for the user or another follow-up request to run more tools.
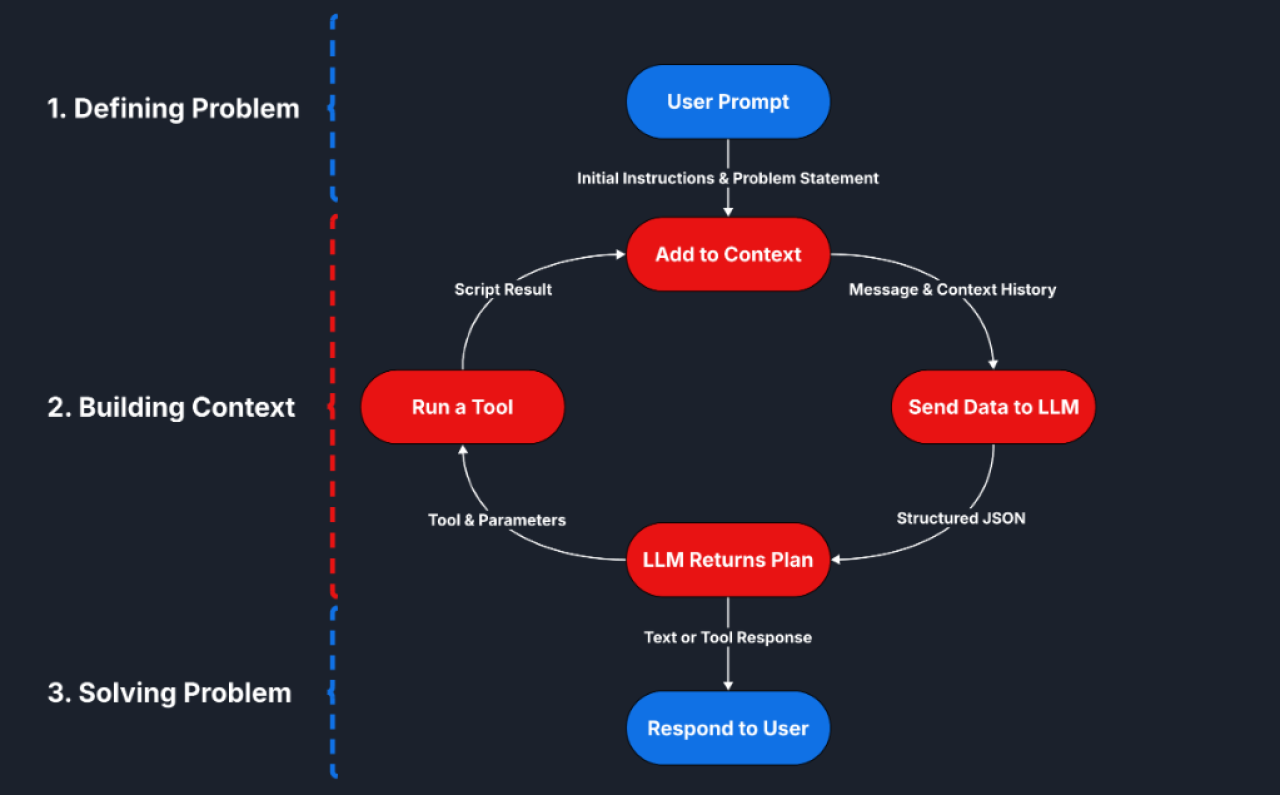
Think of a physical example:
User: Do we have any milk?
FileMaker:
gathers the agent description (ie "You are a domestic agent that supports grocery lists and errands...")
gathers all of the agents' tools and their details (ie "Get Grocery List", "Add to Grocery List", "Check Fridge for Item", "Check Pantry for Item", "Get Item Price", "Locate Stores Nearby", etc)
bundles this with the user's question and sends it all to the model
Model: Call the "Check Fridge for Item" tool with parameter "milk"
FileMaker:
Runs the requested tool with the parameter
Sends the result "milk is in fridge" to the model
Model: Tell the user, "We sure do, we have some milk in the fridge."
FileMaker: Shows the model's final answer to the User
Implementing the Chat Interface
Once your AI account, agents, and tools are set up, you need a user-friendly way to interact with them. We recommend using a Web Viewer inside FileMaker as your chatbot interface. For extra speed and seamless UI, we are using Perform Script on Server with Callback to process requests and display results.
With the Web Viewer, you can:
Prompt the user for input (e.g., "Ask the agent a question")
Display the AI's response in a conversational format
Dynamically switch between agents based on role or context
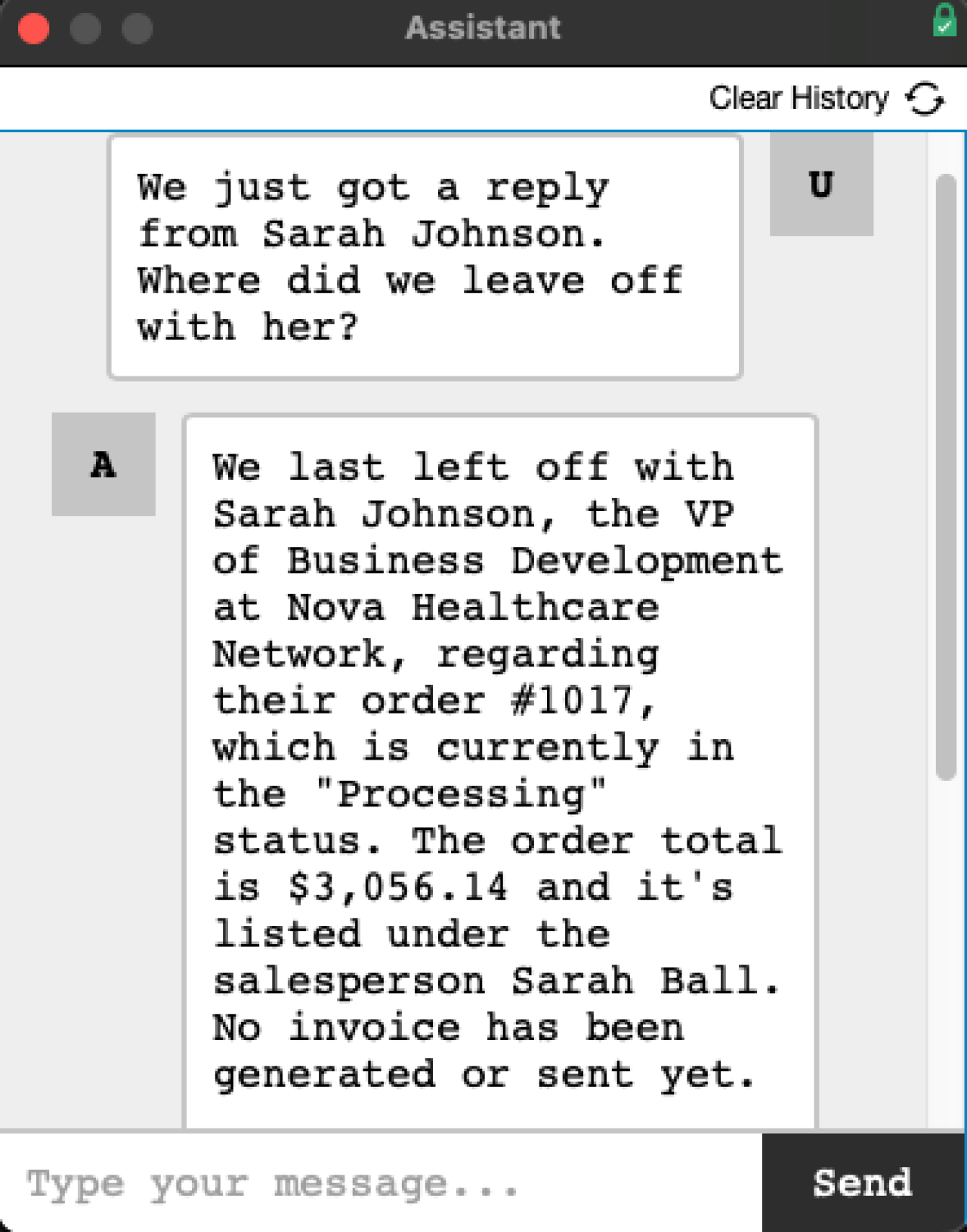
This setup creates a familiar, intuitive experience—like chatting with a real human assistant that knows everything about your FileMaker system (within the bounds of what it's allowed to access).
Drawbacks and Limitations of AI
While AI chatbots offer exciting new capabilities, it's essential to understand their limitations before going all-in:
1. Token-Based Costs
OpenAI's API is not free, and usage is measured in "tokens." Complex prompts, lengthy responses, or high user volume can result in high costs over time.
2. Performance Trade-Offs
AI tools can be slower than traditional scripts, particularly if they rely on network calls or large context windows. Don't expect instant responses every time.
3. Data Security
Sending data to OpenAI means it leaves your FileMaker environment. Sensitive or regulated information should be handled with care, and organizations should be aware of OpenAI's data retention and privacy policies.
4. Reliability
AI should not be tasked with precise, business-critical operations. For example, asking it to summarize notes is a great use case, but you should not ask it to calculate tax returns.
Good problems for AI tools: Creative ideas, suggestions, summarizing info
Bad problems for AI tools: Anything requiring precision, predictability, or accountability
5. Disclosure
If you're building a chatbot focusing on user interactions, it should disclose to users that generative AI chatbots are in use and note their limitations. Users should be aware that they're interacting with a machine, not a person.
6. Training Data and Knowledge Gaps
AI models don't "know" your FileMaker schema unless you explain it in the prompt. And they don't have real-time access to live data unless you provide it.
7. Models Evolve
Finally, remember that AI is a moving target. New models, special features, and pricing structures are changing frequently. What works today may behave differently next month. Build with adaptability in mind.
Real-World Applications
Here are just a few real-world examples where FileMaker + AI chatbots are already showing potential:
Customer Support: Instantly retrieve customer details, ticket statuses, or order histories
Inventory Management: Ask what's in stock, what's low, and what's overdue
Accounting: Review outstanding invoices or flag inconsistencies
Sales: Generate quick summaries of leads, sales performance, or pipeline stages
Project Management: Pull up deadlines, budgets, or task statuses without switching contexts
These use cases not only save time but also improve data accuracy and empower team members to be more self-sufficient.
Conclusion
FileMaker's AI integration is more than just a novelty. It's a powerful tool that helps users interact with data effectively. By combining conversational AI with your business's logic, you turn rigid databases into flexible assistants. The future of FileMaker development lies in creating systems that are more innovative and user-friendly for those who rely on them to meet specific needs, such as driving business growth, automating routine tasks, and supporting personal projects. If you want to implement an AI chatbot in your FileMaker solution, contact us at DB Services. We'd be happy to help!
Did you know we are an authorized reseller for Claris FileMaker Licensing?
Contact us to discuss upgrading your Claris FileMaker software.
Download the Building AI Chatbots File
Please complete the form below to download your FREE FileMaker file.